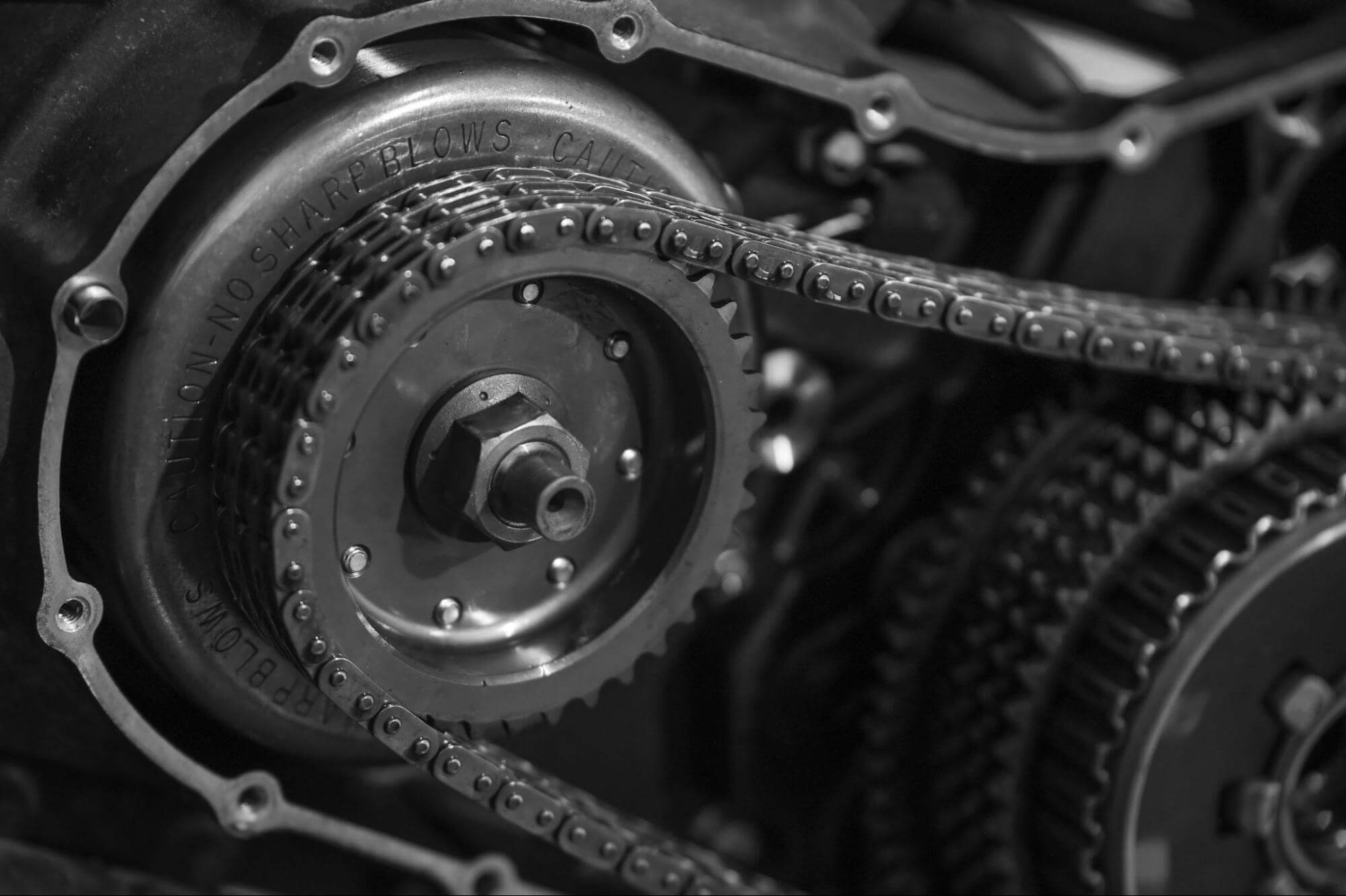
Every motorcycle owner knows the importance of the transmission system. Motorcycle engines can create a massive amount of power, which has to be delivered to the wheels in a controlled manner—the motorcycle’s transmission is the system in charge of this.
The transmission delivers power from the motorcycle’s beating heart—the engine—to the wheels through a series of structures that include the gear set, clutch, and drive system. If even one of these components is faulty or fails, it can cause severe issues for the rest of the transmission and motorcycle.
In this article, we’ll cover how a motorcycle transmission works, motorcycle gearboxes, and telltale signs of failure. We’ll also detail how to fix a failing motorcycle transmission and answer the age-old question of whether it’s better to rebuild or replace it.
How Does A Motorcycle Transmission Work?
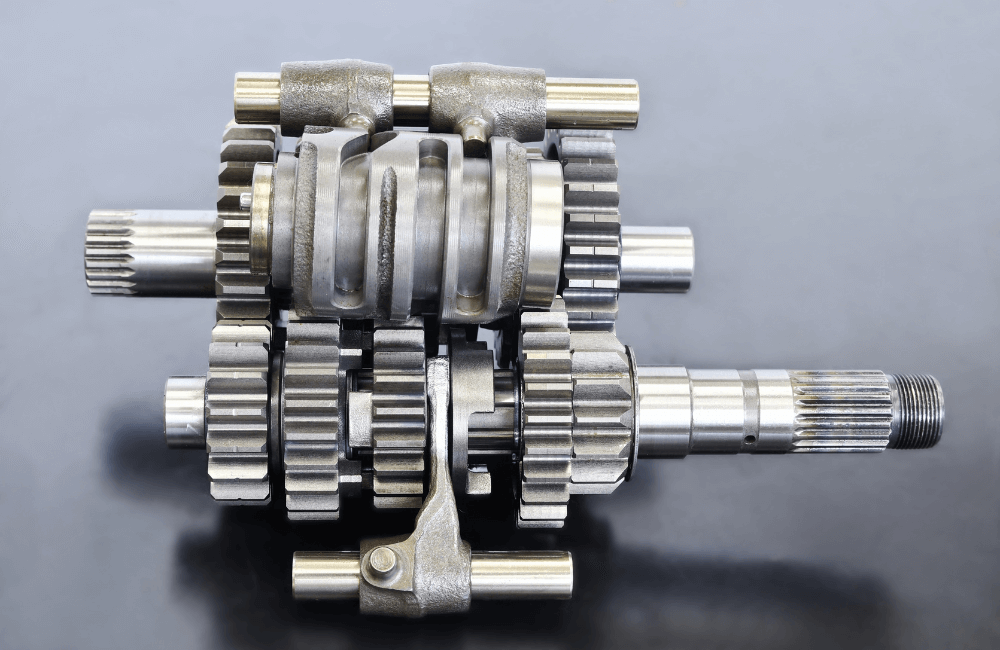
A motorcycle’s transmission is a crucial component of every bike. It allows riders to control the power output from the engine to the rear wheel. Three types of transmissions are generally used in motorcycles: manual, automatic, and semi-automatic.
In these transmission systems, when a gear is selected, two gears are meshed together (in the transmission’s gearbox), providing a gear ratio. These gear ratios allow the transmission to support different directions of power (i.e., from the engine to the rear wheel and vice versa).
When larger gears are selected, they feature more teeth, allowing for higher torque and lower top speeds, while smaller gears with fewer teeth provide higher top speeds and lower torque. These gears can be selected using a lever and a ‘clutch’, which engages/disengages power from the engine crankshaft to the transmission.
Without a clutch, it wouldn’t be possible to control the power from the engine, and the only way to stop the wheels would be to stop the engine, which is impractical. Most motorcycles typically have four to six gears, although small bikes may have as few as two.
Signs Your Motorcycle Transmission is Failing
Identifying the common signs of a motorcycle transmission failure will help you spot issues early, prevent serious damage, and ensure a safer riding experience. Below, we’ve listed the common symptoms to watch out for.
- Any unusual noises or smells
- The transmission keeps ‘slipping’ or having difficulty shifting gears
- Leaking transmission fluid or metal shavings in the fluid
- Any problems with the clutch, including clunking sounds or burning smells
- Inconsistent performance when riding
- The motorcycle’s dashboard has warning lights
Causes of Motorcycle Transmission Failure
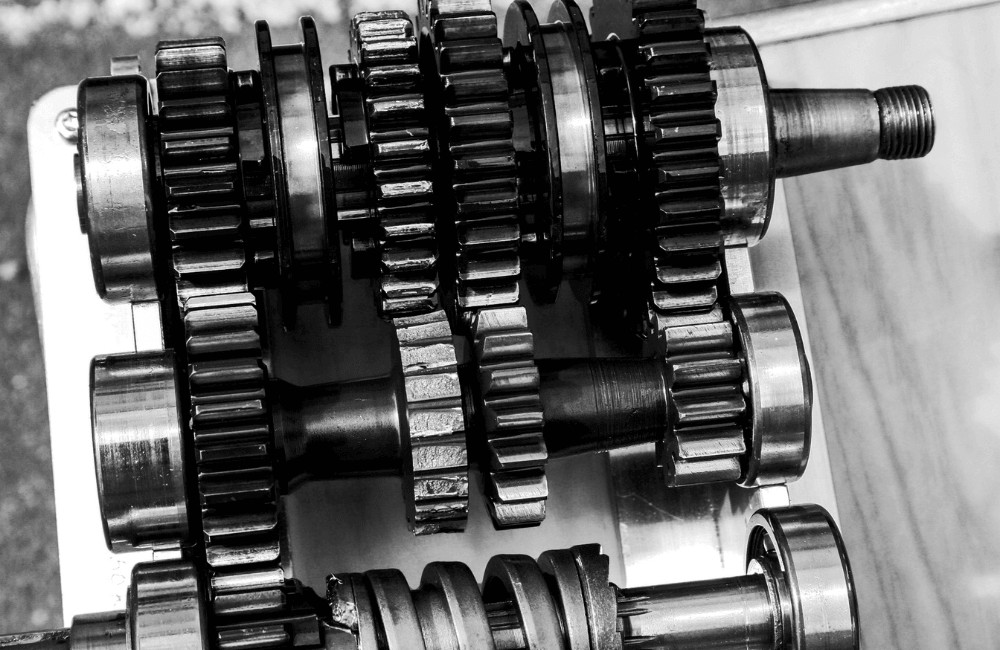
Motorcycle transmission failure can result from various factors or a combination of problems. The most common causes include:
- Lack of maintenance of transmission components can lead to wear and tear and, in severe cases, extreme damage.
- Transmission gears can wear out due to high mileage or aggressive riding, resulting in difficulty shifting, gear slippage, and transmission failure.
- Prolonged exposure to excessive heat/high temperatures can degrade transmission fluid in a motorcycle, causing components to wear out faster.
- It’s possible for components to fail, like the synchronisers (synchros) or gear teeth, to then go on and damage other parts.
- Although it’s uncommon, poor quality control can lead to manufacturing defects, such as improperly machined gears, which can lead to transmission failure in new motorcycles.
- In modern motorcycles that utilise advanced electronic systems, faulty sensors can provide incorrect data to the transmission, resulting in improper shifting and other issues if not properly tuned.
Preventative Measures
As the adage goes, the best cure is prevention, and the best way to fix a motorcycle transmission failure is to avoid it in the first place. Below, we’ve listed different preventative measures that can be taken to help avoid transmission failure.
- Following the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule and staying on top of major servicing can help prevent transmission failure.
- Using the clutch properly when shifting through gears can prevent unnecessary wear and tear.
- Regularly monitor fluid levels, including checking the transmission fluid—top up and replace it when needed.
How To Fix A Failed Motorcycle Transmission

Fixing a failed motorcycle transmission requires specialised mechanical knowledge, diagnostic skills, and access to a workspace with specialised tools. Below, we’ve outlined the general steps to diagnosing and repairing a failed transmission.
It’s important to keep in mind that a failing transmission is usually a complex issue that requires a professional mechanic. In those cases, we recommend booking the bike with a qualified mechanic, as they can easily diagnose and perform repairs. Fixing the bike yourself without the proper tools or knowledge can also be a safety risk.
Diagnosis & Preparation
The first step to fixing a failed transmission is diagnosis. A failed transmission could be the result of a combination of factors and be found in different places, as it is made up of multiple components and structures.
The first thing you want to do is identify any symptoms. This includes noting down the symptoms, like unusual noises, weird smells, and difficulty with gears. This can help pinpoint the exact issue.
We also recommend inspecting the transmission fluid and checking for any leaks or abnormalities. Any metal shavings in the liquid can indicate internal damage. If safe, we also recommend taking the motorcycle on a test ride to observe any issues firsthand.
Once you’ve diagnosed the issue, preparation is the next step. Gather all the tools required, including wrenches, screwdrivers, a motorcycle lift or stand, and any other specialised tools for the repairs. We also recommend finding the motorcycle’s service manual for specific instructions for working on the specific transmission of the make and model.
Disassembly
After diagnosing the problem and preparing all the tools you need, you’ll need to start disassembly and start removing any components that obstruct access to the transmission.
Before accessing the transmission, it’s important to drain the transmission fluid and disconnect the shifter linkage and any electric connectors, along with disassembling the required components.
Depending on your bike’s make and model, you may also need to remove the engine from the frame or access the transmission by removing the side covers.
Inspection & Replacement
After disassembly, it’s time to start inspecting all the transmission components, including the gearbox and clutch. Carefully check all the gears, bearings, and other internal components for damage and wear, replacing components if necessary.
On the clutch, we recommend inspecting the clutch plates, springs, and baskets for wear. It’s also critical to examine the synchronisers and shift forks—if any wear is present, replace them for smooth gear engagement.
Reassembly & Testing
After performing the required repairs and replacements, carefully reassemble the transmission components and reinstall everything back onto the bike’s frame, following the manufacturer’s service manual.
Once reassembled, it’s important to test the motorcycle by starting it and letting it idle. During this process, listen for any unusual noises and check for leaks. If everything seems alright, take the motorcycle for a test ride and make any required adjustments.
It’s key to remember that the above steps are just a general guide for diagnosing and repairing a motorcycle’s transmission. The specific procedure will depend on the problem and the bike’s make and model.
When Is It Better To Rebuild or Replace?
Deciding whether to rebuild or replace a motorcycle’s transmission will depend on the circumstances, extent of the damage, cost considerations, and availability of parts. In the end, it’ll depend on personal preference, but below, we’ve outlined when you should rebuild vs. replace.
If the motorcycle’s transmission has minor to moderate wear or damage, such as worn bearings, rebuilding might be the better option as it’ll be cost-effective. This allows you to replace worn or broken components instead of replacing everything.
Rebuilding is generally less expensive than replacing the entire transmission, especially if only one or a few components need to be replaced. However, it’s important to remember that depending on the complexity and part availability, rebuilding can take weeks or months.
If a motorcycle’s transmission has suffered extensive damage, such as multiple broken components or severe internal wear, replacement is often more practical and less time-consuming.
If the cost of a rebuild approaches the cost of a replacement, it’s always better to just replace the whole transmission. When buying a replacement from a reputable supplier, it might also come with a warranty, which is important to consider.
Professional Repair Work and Servicing at Taverner

At Taverner Motorsports, we offer professional motorcycle repairs and motorcycle servicing, with a passion for British and Harley-Davidson bikes, including transmission work. So, if you’re concerned that your motorcycle’s transmission or gearbox is failing, contact us today and request a quote.
Our team has over 40 years of experience in the industry and is experienced in all aspects of motorcycle repair and servicing. We also understand how important a motorcycle can be to its owner and its sentimental value. When you bring your bike in for repair work, you can rest assured that we’ll treat it with the utmost care and respect.
At our workshop, we also understand the importance of using high-quality parts for repairs and servicing. When you come to us for work on your motorcycle, we’ll always give you the option of using genuine or aftermarket components. We’ll also be transparent throughout the process, informing you of any repairs required, estimated costs, and a timeline for completion.
If you require professional repair work or are concerned about your bike’s transmission, contact us today for a quote. The Taverner Motorsports team would also be happy to answer any questions you may have.